We use cookies that are strictly necessary for the operation of this website as well as statistical cookies that allow us to anonymously know how users interact with the website in order to optimize your user experience.
These cookies can be set at any time from the publication.
TABLE OF CONTENT
- 1
- Prospects:...Prospects: Jean-Paul Agon, Chairman of the Board of Directors of L’OréalProspects: Jean-Paul Agon, Chairman of the Board of Directors of L’Oréal - Page 22
- Prospects: Nicolas...Prospects: Nicolas Hieronimus, Chief Executive Officer of L’OréalProspects: Nicolas Hieronimus, Chief Executive Officer of L’Oréal - Page 33
- Chapter 1...Chapter 1 : Presentation of the Group – Integrated ReportChapter 1 : Presentation of the Group – Integrated Report - Page 5
page 5 TO 52
- 1.1. The...61.1. The L’Oréal Group: the fundamentals1.1. The L’Oréal Group: the fundamentals - page6
- 1.2. L’Oréal,...141.2. L’Oréal, a value-creating model1.2. L’Oréal, a value-creating model - page14
- 1.3. 2022...361.3. 2022 Financial Results and Corporate Social Responsibility commitments1.3. 2022 Financial Results and Corporate Social Responsibility commitments - page36
- 1.4. A...501.4. A tailored, agile and responsive organisation1.4. A tailored, agile and responsive organisation - page50
- 1.5. Internal...511.5. Internal Control and risk management system1.5. Internal Control and risk management system - page51
- Chapter 2...Chapter 2 : Corporate governanceChapter 2 : Corporate governance - Page 53
page 53 TO 116
- 2.1. Framework...542.1. Framework for the implementation of corporate governance principles2.1. Framework for the implementation of corporate governance principles - page54
- 2.2. Composition...572.2. Composition of the Board at 31 December 20222.2. Composition of the Board at 31 December 2022 - page57
- 2.3. Organisation...722.3. Organisation and modus operandi of the Board of Directors2.3. Organisation and modus operandi of the Board of Directors - page72
- 2.4. Remuneration...912.4. Remuneration of directors and corporate officers2.4. Remuneration of directors and corporate officers - page91
- 2.5. Summary...1142.5. Summary table of the recommendations of the AFEP‑MEDEF Code which have not been applied2.5. Summary table of the recommendations of the AFEP‑MEDEF Code which have not been applied - page114
- 2.6. Summary statement...1152.6. Summary statement of trading by directors and corporate officers in L’Oréal shares in 20222.6. Summary statement of trading by directors and corporate officers in L’Oréal shares in 2022 - page115
- 2.7. Statutory...1152.7. Statutory Auditors’ Special Report on regulated agreements2.7. Statutory Auditors’ Special Report on regulated agreements - page115
- Chapter 3...Chapter 3 : Risk factors and risk managementChapter 3 : Risk factors and risk management - Page 117
page 117 TO 150
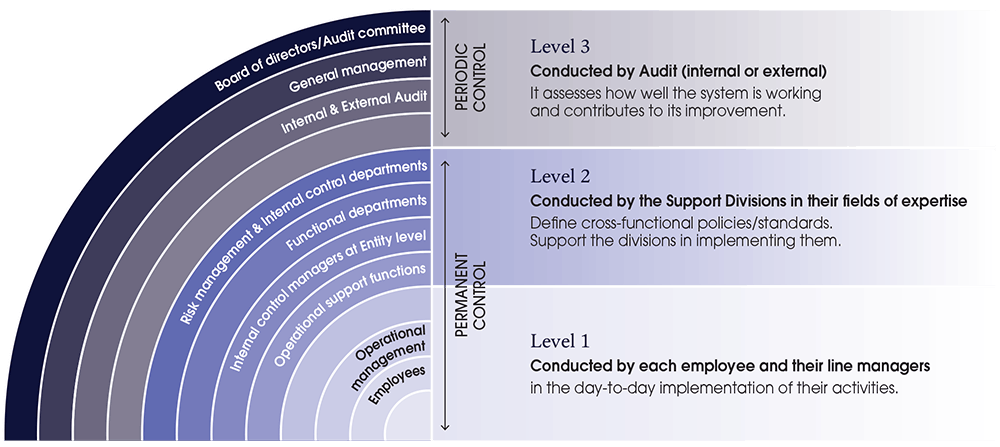
- 3.1. Definition...1183.1. Definition and objectives of Internal Control3.1. Definition and objectives of Internal Control - page118
- 3.2. Components...1193.2. Components of the Internal Control and Risk Management system3.2. Components of the Internal Control and Risk Management system - page119
- 3.3. Preparing...1243.3. Preparing and processing accounting and financial information3.3. Preparing and processing accounting and financial information - page124
- 3.4. Vigilance...1263.4. Vigilance Plan3.4. Vigilance Plan - page126
- 3.5. Risk...1413.5. Risk factors and risk management3.5. Risk factors and risk management - page141
- Chapter 4...Chapter 4 : Social, environmental and societal responsibilityChapter 4 : Social, environmental and societal responsibility - Page 151
page 151 TO 252
- 4.2. Main...1604.2. Main non-financial risks4.2. Main non-financial risks - page160
- 4.3. Policies,...1624.3. Policies, performance indicators and results4.3. Policies, performance indicators and results - page162
- 4.4. L’Oréal...2314.4. L’Oréal for the Future: 2022 results4.4. L’Oréal for the Future: 2022 results - page231
- 4.5. Methodological...2324.5. Methodological notes4.5. Methodological notes - page232
- 4.6....2394.6. Cross-reference tables, including NFIS and GHG balance4.6. Cross-reference tables, including NFIS and GHG balance - page239
- 4.7. Statutory...2444.7. Statutory Auditor's Reports4.7. Statutory Auditor's Reports - page244
- Chapter 5...Chapter 5 : 2022 Consolidated Financial StatementsChapter 5 : 2022 Consolidated Financial Statements - Page 253
page 253 TO 316
- 5.1. Compared...2545.1. Compared Consolidated Income Statements5.1. Compared Consolidated Income Statements - page254
- 5.2. Consolidated...2555.2. Consolidated Statement of Comprehensive Income5.2. Consolidated Statement of Comprehensive Income - page255
- 5.3. Compared...2565.3. Compared Consolidated Balance Sheets5.3. Compared Consolidated Balance Sheets - page256
- 5.4. Consolidated...2575.4. Consolidated Statements of Changes in Equity5.4. Consolidated Statements of Changes in Equity - page257
- 5.5. Compared...2595.5. Compared Consolidated Statements of Cash Flows5.5. Compared Consolidated Statements of Cash Flows - page259
- 5.6. Notes...2605.6. Notes to the Consolidated Financial Statements5.6. Notes to the Consolidated Financial Statements - page260
- 5.7. Main...3105.7. Main consolidated companies at 31 December 20225.7. Main consolidated companies at 31 December 2022 - page310
- 5.8. Statutory...3135.8. Statutory Auditor's Report on the Consolidated Financial Statements5.8. Statutory Auditor's Report on the Consolidated Financial Statements - page313
- Chapter 6...Chapter 6 : Parent company financial statementsChapter 6 : Parent company financial statements - Page 317
page 317 TO 344
- 6.1. Compared...3186.1. Compared income statements6.1. Compared income statements - page318
- 6.2. Compared...3196.2. Compared balance sheets6.2. Compared balance sheets - page319
- 6.3. Changes...3206.3. Changes in shareholders’ equity6.3. Changes in shareholders’ equity - page320
- 6.4. Statements...3216.4. Statements of cash flows6.4. Statements of cash flows - page321
- 6.5. Notes...3226.5. Notes to the financial statements of L’Oréal S.A.6.5. Notes to the financial statements of L’Oréal S.A. - page322
- 6.6. Other...3376.6. Other information relating to the financial statements of L’Oréal S.A.6.6. Other information relating to the financial statements of L’Oréal S.A. - page337
- 6.7....3386.7. Five-year financial summary6.7. Five-year financial summary - page338
- 6.8. Equity...3396.8. Equity investments (main changes including shareholding threshold changes)6.8. Equity investments (main changes including shareholding threshold changes) - page339
- 6.9. Statutory...3406.9. Statutory Auditor's Report on the Financial Statements6.9. Statutory Auditor's Report on the Financial Statements - page340
- Chapter 7...Chapter 7 : Share capital and stock market informationChapter 7 : Share capital and stock market information - Page 345
page 345 TO 364
- 7.1. Information...3467.1. Information relating to the Company7.1. Information relating to the Company - page346
- 7.2. Information...3487.2. Information concerning the share capital7.2. Information concerning the share capital - page348
- 7.3. Shareholder...3507.3. Shareholder structure7.3. Shareholder structure - page350
- 7.4....3537.4. Long-term incentive plans7.4. Long-term incentive plans - page353
- 7.5. The...3587.5. The L’Oréal share/the share market7.5. The L’Oréal share/the share market - page358
- 7.6. Information...3637.6. Information and shareholder dialogue policy7.6. Information and shareholder dialogue policy - page363
- Chapter 8...Chapter 8 : Annual General MeetingChapter 8 : Annual General Meeting - Page 365
page 365 TO 386
- 8.1. Draft resolutions and Report of the Board of Directors to the Ordinary...3668.1. Draft resolutions and Report of the Board of Directors to the Ordinary and Extraordinary General Meeting to be held on Friday 21 April 20238.1. Draft resolutions and Report of the Board of Directors to the Ordinary and Extraordinary General Meeting to be held on Friday 21 April 2023 - page366
- 8.2. Statutory...3858.2. Statutory Auditor's Report8.2. Statutory Auditor's Report - page385
- 9.1. Statutory...3889.1. Statutory Auditors9.1. Statutory Auditors - page388
- 9.2. Historical...3889.2. Historical financial information included by reference9.2. Historical financial information included by reference - page388
- 9.3. Declaration by the person...3889.3. Declaration by the person responsible for the Universal Registration Document and the Annual Financial Report9.3. Declaration by the person responsible for the Universal Registration Document and the Annual Financial Report - page388
- 9.4....3899.4. Cross-reference table with the Universal Registration Document9.4. Cross-reference table with the Universal Registration Document - page389
- 9.5. Annual...3919.5. Annual Financial Report cross-reference table9.5. Annual Financial Report cross-reference table - page391
- 9.6. Cross-reference table with...3919.6. Cross-reference table with the AMF tables on the remuneration of directors and corporate officers9.6. Cross-reference table with the AMF tables on the remuneration of directors and corporate officers - page391
- 9.7. Management...3929.7. Management Report cross-reference table9.7. Management Report cross-reference table - page392
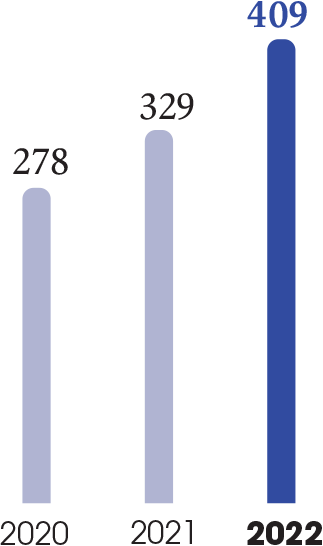
In 2022, the Internal Audit Department carried out 51 assignments, 26 of which involved entities (commercial entities, factories, international marketing departments, R&I) and 17 of which were on targeted processes at Group, Zone or Country level. In addition, two specific assignments were devoted to certain objectives of the L’Oréal for the Future programme, three were dedicated to the management of key projects and three were carried out on the cyber security programme.
Each audit assignment results in a report that sets out the corresponding findings and risks, and that proposes an action plan and recommendations for the audited entity. The Internal Audit Department monitors and measures these action plans, then reports the rate of progress to the Departments in question.
To conduct its work, Internal Audit relies on the Group’s integrated ERP software. It has developed a number of specific transactions to improve the identification of potential weaknesses in sensitive processes. Data analysis capabilities are strengthened each year. They enhance the standard analyses developed by Internal Audit and the use of dashboards and analysis tools that the businesses are continually developing for their own management needs.
To carry out its work, the Internal Audit Department uses an integrated GRC (Governance, Risk, Compliance) tool, which enables it to consolidate in real-time the progress made on the action plans of audited entities. Shared with the Internal Control function, this tool represents an integrated collaborative platform for the implementation of action plans.
In addition to its role of monitoring the application of the Internal Control system, the Internal Audit Department carries out cross-functional analyses with regard to possible Internal Control weaknesses based on findings noted during its assignments. These analyses direct the work of the Internal Control Committee and identify the priority areas for improvement and strengthening of procedures.
The achievement of the audit plan, the results of assignments and the progress of the action plans are presented to General Management on a regular basis and to the Audit Committee and the Statutory Auditors annually.
The Global IT Department
The Group’s Global IT Department determines the strategic orientations of its IT systems. In particular, it implements ERP, a management software which is used by the vast majority of the Group’s commercial subsidiaries, factories and logistics services. It also supports the digital transformation of the Group by developing the use of Cloud services (SaaS, IaaS, PaaS)and connected objects.
Within the Department, the Information Systems Security Department manages the Information Systems Security Policy. Consistent with market standards (ISO 27001/27002, NIST), this policy covers the main topics of IT security, including the protection of personal data. It describes general principles to be applied for each topic. This ensures that the Group’s Information Systems teams, and by extension, all employees, share clear objectives, best practices and levels of control that are appropriate for the risks (notably, the risk of cyberattacks). This policy is accompanied by an independent information systems security audit programme and two codes of practice: the Information and Communication Technologies Code of Practice, and the Code of Good Practice for the use of Social Media.
The Operations Department
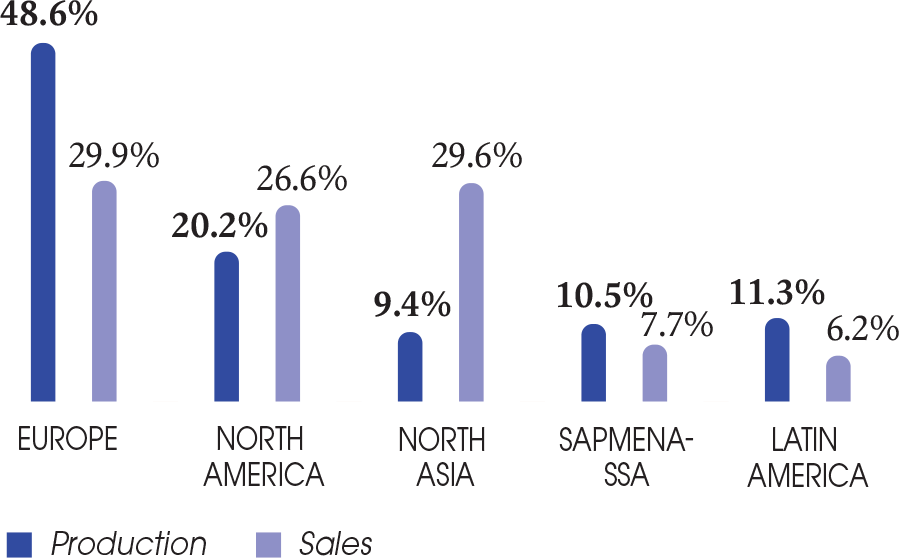
This division comprises the Innovation, Product Packaging and Development, Quality, EHS (Environment, Health, Safety), Production management and operational excellence, Purchasing, Supply Chain, Information Systems (production)and industrial strategy departments. It defines the overall Operations strategy worldwide and defines the standards and methods applicable in the areas of quality, safety and the environment for deployment in all the countries in which the Group operates. It manages the Group’s comprehensive strategy to enable the Operations teams in the operational Divisions and the Zones to implement innovation, quality, security, environmental manufacturing and supply chain policies that are relevant to the markets.
In line with the Group’s Code of Ethics, buyers have had access to a practical and ethical guide, “The Way We Work with Suppliers”, since 2011. This guide aims to help all employees in their relationships with the Group’s suppliers. Buyers also complete e-learning modules based on the Group’s “The Way We Compete” and “The Way We Prevent Corruption” guides.
The standard for managing suppliers and tender procedures specify the conditions for competitive tendering and for the registration of the main suppliers. The general terms of purchase form the framework for transactions with the suppliers. The “Purchase Commitments and Order Management” standard facilitates and strengthens control of spending and investments.
In the area of supply chain, the main tasks are to define and apply the sales planning, demand management and customer service development and control processes. The methods used include managing physical order fulfilment, applying the general terms of sale, following-up orders, managing customer returns and customer disputes, as well as accounts receivable collection procedures. Measures are also recommended for the management of distribution centres and inventories, subcontracting, product traceability, business continuity plans and transportation.